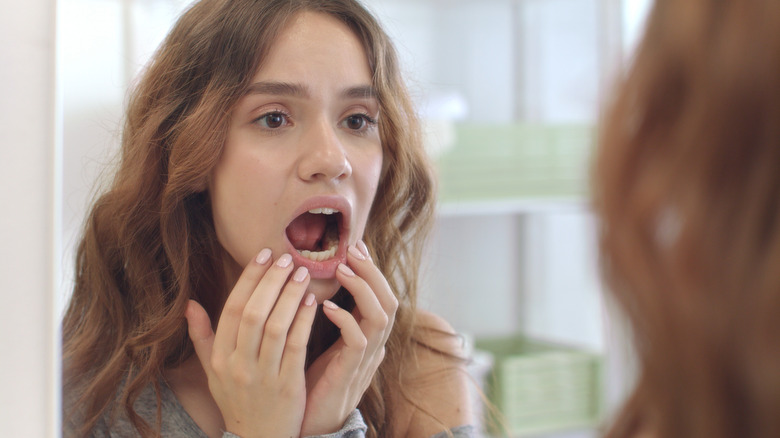
Suppose you have noticed white spots on your gums. In that case, it is important to pay attention to their appearance — they can be a sign of various conditions, ranging from minor issues like canker sores, oral thrush, oral lichen planus, leukoplakia, and vitamin deficiencies, to more serious conditions such as oral cancer, says Healthline.
A range of symptoms can also accompany the spots. Depending on the cause, pain or discomfort is a common symptom that may accompany white spots on the gums. The pain may be mild to severe and may be aggravated by eating, drinking, or brushing the teeth. Inflammation or swelling of the gums is another symptom that may make it difficult to speak or brush the teeth. Some conditions that cause white spots on the gums may also lead to changes in taste or sensation in the mouth.
While many cases of white spots on the gums are not serious, it’s always better to be cautious and get it checked out by your doctor. This is especially important if your symptoms are severe or won’t go away. Depending on the underlying cause, treatment may include medication, dietary changes, or surgery.
Common causes of white spots on the gums
Canker sores are a common culprit behind white spots on the gums. According to the Mayo Clinic, canker sores are small, painful ulcers that can develop on the gums or other soft tissues in the mouth. They often have a white or yellow center surrounded by a red border. Common causes of canker sores include stress, menstruation, and vitamin deficiencies. Oral thrush is another common cause. This fungal infection can cause white patches to also develop in various other mouth areas, including the gums, says Healthline. It is most often seen in babies but can affect adults as well, especially those with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly or people with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy.
Leukoplakia is a condition that causes white or gray patches to develop on the gums, tongue, or other areas of the mouth, explains the Mayo Clinic. It is often associated with tobacco use and can sometimes be a precancerous condition. Oral lichen planus can also cause white spots to develop on the gums and other areas of the mouth, according to the Cleveland Clinic. This chronic inflammatory condition affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, including the gums, tongue, and cheeks. It is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy tissues. The white spots may appear as lacy, raised patches or lines, accompanied by redness or inflammation. Lastly, white spots on the gums can be a sign of oral cancer, which can occur in the mouth, tongue, lips, gums, or throat, says Medical News Today. Common symptoms include a persistent sore or lump in the mouth, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and unexplained bleeding.
Treatment for white spots on the gums
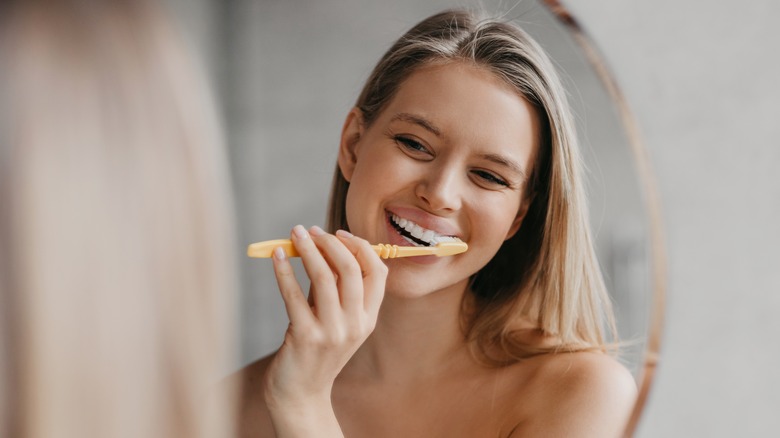

The treatment for white spots on the gums will vary depending on the underlying cause. Canker sores usually heal on their own within a week or two, says the Mayo Clinic. Over-the-counter medications such as benzocaine or hydrogen peroxide can help relieve pain and promote healing. In severe cases, a prescription medication may be necessary.
Oral thrush is usually treated with antifungal medication, such as clotrimazole or fluconazole, says Healthline. The medication may be applied topically to the affected area or taken orally. If leukoplakia is the cause of your white spots and is associated with tobacco use, quitting smoking or other tobacco products may be recommended, per the Mayo Clinic. If the condition is severe or precancerous, surgical removal of the affected area may be necessary.
Treatment for oral lichen planus typically involves managing symptoms and controlling inflammation. This may include topical or systemic corticosteroids or other medications that help reduce inflammation, says the Cleveland Clinic.
If white spots on the gums are caused by vitamin deficiencies, supplements or dietary changes may be recommended. In cases of oral cancer or other more serious conditions, treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. Following the recommended treatment plan and attending regular follow-up appointments with a dentist or healthcare provider is important to monitor the condition.




